What Is the Functional Unit of a Muscle Cell
The sarcomere is considered as the functional unit of contraction. Sarcomeres are organized in series to make up a myofibril.

Pin By Warwick Nurse On Biology Muscle Contraction Biology Notes Biology
Sarcomeres are connected end to end by Z lines along the length of each myofibril.

. Hence The functional unit of the contractile system of a striated muscle is sarcomere. The sarcomere is the functional unit of a striated muscle. Each smooth muscle cell is under.
Regarding this what is the basic functional unit of a muscle. The sarcomere is the functional unit of the muscle fiber. Gap junctions between the cells O Multi-unit.
The main function of muscle cells is to produce contractions of the muscle. Muscles are composed of tubular cells called myocytes known as muscle fibers in striated muscle and these cells in turn contain many chains of myofibrils. Thick filaments composed primarily of the contractile protein myosin and thin filaments composed primarily of the contractile protein actin.
Muscle cells rarely act alone muscle organs operate on principle of graded strength Motor Units the functional unit of muscle system motor unit individual motor neuron and all muscle cells that it innervates the axon of a motor neuron usually branches on entering a muscle bundle and a single axon may innervate a few to 100s of muscle. The functional unit for muscle contraction like sacromeres in skeletal muscles C A protein that binds oxygen in the cardiac muscle cell D Complex membrane junctions that include desmosomes and gap junctions. It can be observed on microscope slides due to the striated nature of both skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle.
Muscle cells have a membrane called the sarcolemma that allows impulses to travel along the bodys muscles. Threadlike structures made of myosin and actin. Muscle Cell Definition.
Since most of the human bodys muscles act as voluntary muscles. The muscles of the gut are involved in peristalsis-what is the kind of functional unit to describe these cells and how is their action coordinated. Gap junctions between the cells Single-unit.
This means it is the most basic unit that makes up our skeletal muscle. A muscle cell is also known as Myocyte which is a specialized animal cell that can shorten its length by using a series of motor proteins especially arranged in the cell. The repetition of sarcomeres within the muscle fiber gives the muscle its characteristic striated pattern.
Answered Feb 3 2021 by Tonee0073. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. So the correct answer is Sarcomere.
A sarcomere is the functional unit contractile unit of a muscle fiber. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Even in eukaryotic multicellular organisms different organs have specific cell type which perform specific functions this also prove the.
A sarcomere is the basic functional within muscle cells. Muscles function to produce force and motion. The myofibrils are composed of actin and myosin filaments repeated in units called sarcomeres which are the basic functional units of the muscle fiber.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. A muscle consists of fibers of muscle cells surrounded by protective tissue bundled together many more fibers all surrounded in a thick protective tissueA muscle uses ATP to contract and shorten producing a force on the objects it is connected to. Even in eukaryotic multicellular organisms different organs have specific cell type which perform specific functions this also prove the.
Impulses are sent through the nervous system along the muscle cells and cause the muscle to contract. Start studying FUNCTIONAL UNIT OF THE MUSCLE. The portion of the myofibril between two successive Z lines is considered as a sarcomere.
The sarcomere is defined as spanning from Z-line to Z-line described in detail below only a few micrometers long and consists of an A band containing myosin thick filaments which is. The sarcomere is the smallest functional unit of a skeletal muscle fiber and is a highly organized arrangement of contractile regulatory and structural proteins. A muscle is a group of muscle tissues which contract together to produce a force.
The sarcomere itself is bundled within the myofibril that runs the entire length of the muscle fiber and attaches to the sarcolemma at its end. The unit between two Z lines is called a sarcomere. While several associated proteins help actin and myosin form thick and thin filaments which slide past each other to contract small units of a muscle cell.
The sarcomere of striated muscles. Elongated contractile threads found in striated muscle cells. Depicted in Figure 1 is the sarcomere which is the basic contractile unit of striated muscle.
Each smooth muscle cell is under direct neuronal control O Multi-unit. As illustrated in Figure 2-5 each sarcomere contains two types of myofilaments. As myofibrils contract the entire muscle cell contracts.
Communicated to the inner muscle cell via the T-tubule system Action potential transverse a muscle fiber via the t-tubules and are ultimately responsible for the release of calcium from the SR Sarcomere - Basic contractile unit of the muscle. This unit is distinctive in some types of muscle tissue. Each muscle fiber is encased in a cell membrane.
A muscle cell known technically as a myocyte is a specialized animal cell which can shorten its length using a series of motor proteins specially arranged within the cell. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. And several other associated proteins help actin and myosin form thin and thick filaments that slide past each other in order to contract small units of the muscle cell.
Each fiber must possess many functional contractile units. Sarcomere is the functional unit of muscle fiber which are organized in series to make up myofibril. The basic structural and functional unit of a muscle cell is the sarcomere which consists of thin filaments of the protein actin and thicker filaments of the protein myosin.
It is the shortening of these individual sarcomeres that lead to the contraction of individual skeletal muscle fibers and ultimately the whole muscle.

Biology 202 Pringle Flashcards Muscular System Studyblue Muscular System Physiology Anatomy And Physiology

Pin By Jessica Joyce On Systems Musculoskeletal Human Anatomy And Physiology Body Muscle Anatomy Medical School Inspiration
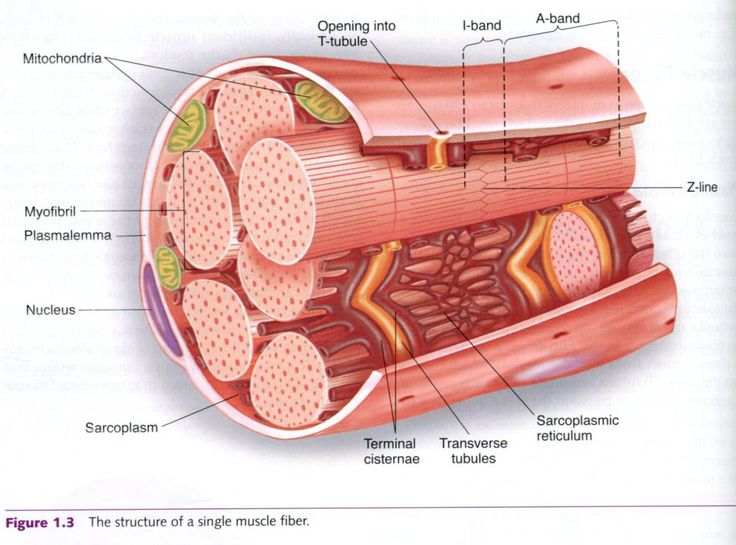
Myofibrils Complete Soccer Training Functional Anatomy Of The Skeletal Muscle Muscle Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Smooth Muscle Tissue

Understand Plant Cell With Diagram Cell Diagram Plant Cell Plant Cell Structure

Sarcomere Definition Structure Function And Quiz Biology Dictionary Skeletal Muscle Biology Skeletal

Muscle Cell Comparison Muscular System Human Anatomy And Physiology Human Muscle Anatomy

Muscles Lesson Skeletal Muscle Muscle Hypertrophy Muscular System

Sarcomere Human Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy And Physiology Muscle

Muscle Structure And Control Of Contraction Muscle System Mcat Content

Chapter 9 Muscles And Muscles Tissue Human Anatomy And Physiology Muscle Tissue Muscle

Pin By Renuka Dhumal On Science Neurons Noise Pollution Taxon
19 4 Muscle Contraction And Locomotion Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition

Muscle Fiber Model Motor Neuron Myeline Sheath Node Of Ranvier Synaptic Terminal Synaptic Cleft E Human Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Medical Anatomy

Muscle Cell Myocyte Definition Function Structure Biology

A Motor Unit Human Body Activities Muscle Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology

Cumulative Topic 6 Microanatomy Of Myofiber Body Muscle Anatomy Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Muscle Anatomy

Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review Physiology Nursing School Studying Human Anatomy And Physiology

Contraction In The Simplest Sense Is Shortening Of A Muscle Fibre When Muscles Receive Stimulation From The Ne Muscle Structure Muscle Diagram Medical Anatomy

Comments
Post a Comment